Glocalizing Sustainable Tourism: Sri Lanka’s Strategy for Italian Inbound Travelers

 By Prof DAC Suranga Silva Professor in Tourism Economics, Sustainable Tourism Unit (STU) University of Colombo, Sri Lanka Emails: drsuranga@econ.cmb.ac.lk; drsuranga3@gmail.com
By Prof DAC Suranga Silva Professor in Tourism Economics, Sustainable Tourism Unit (STU) University of Colombo, Sri Lanka Emails: drsuranga@econ.cmb.ac.lk; drsuranga3@gmail.com
- Professor: Tourism Economics, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka
- Coordinator: Sustainable Tourism Unit (UOC-STU), Faculty of Arts, University of Colombo
- Secretary General: Tourism and Hospitality Educators and Researchers Association of Asia (THERAA)
- Affiliated Member: International Association of Universities of the Third Age(IAIUTA)
- A Lead-Trainer: Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) for Sustainable Tourism Destination Management
- Chief Editor: Journal of Tourism Economics and Applied Research (JTEAR)
- Chief Editor: International Journal of Sustainable Tourism (IJST)
- Founding Coordinator: Postgraduate Diploma Leading Master in Tourism Economics and Hotel Management, University of Colombo
An Overview of Italian Outbound Tourism and Its Key Characteristics
Italian outbound tourism is primarily directed towards European destinations. Top choices of Italian outbound tourists are mainly Spain, France and Germany in Europe.
There has been a steady recovery after easing travel restrictions of COVID pandemic by year 2023, returning to the pre-pandemic levels at 35.2 million trips, reflecting a 25.7% rise from 2022.Italian outbound tourism experienced a sharp decline due to the COVID-19 pandemic, with trips reducing from 35.5 million in 2019 to 16 million in 2020, marking a 54.9% decrease.
Table 1: Italian Outbound Tourism
| Year | Total Outbound Trips (millions) | Percentage Change of Outbound Tourist Trips from Previous Year | Outbound Tourism Expenditure (Billion Euros | Percentage Change of Outbound Tourism Expenditure from Previous Year |
| 2019 | 35.5 | – | 30.0 | |
| 2020 | 16.0 | -54.9% | 13.5 | -55% |
| 2021 | 18.5 | +15.6% | 15.5 | +15% |
| 2022 | 28.0 | +51.4% | 25.0 | +61% |
| 2023 | 35.2 | +25.7% | 30.0 | +20% |
Source: Global Data’s “Italy Source Tourism Insight” Report 2022, 2023.
In 2022, Italian tourists spent almost $26.9 billion abroad when the total number of outbound trips from Italy was 35.22 million in 2022. In the second quarter of 2024, Italian outbound tourists spent nearly $4.29 billion for EU destinations alone. In 2023, Italian outbound tourism expenditure totaled $34.2 billion. The total number of outbound trips from Italy also increased to 33.8 million in 2023
In 2022, Italian tourists spent almost $26.9 billion abroad when the total number of outbound trips from Italy was 35.22 million in 2022. In the second quarter of 2024, Italian outbound tourists spent nearly $4.29 billion for EU destinations alone. In 2023, Italian outbound tourism expenditure totaled $34.2 billion. The total number of outbound trips from Italy also increased to 33.8 million in 2023
Table 2: Italian Outbound Tourism: Global vs. European Contribution (2023)
| Category | European Contribution | Global Contribution |
| Top Destinations | Spain (1.5M trips), France (1.2M trips), Germany (773K trips) | Spain, USA, France |
| Share of Outbound Trips | Europe: ~70% of total outbound trips | Non-European destinations: ~30% |
| Expenditure
(Top Destinations) |
Spain (€3.4B), France (€2.5B), Germany (€1.8B) | USA (€3.2B), Spain (€3.4B), France (€2.5B) |
| Total Outbound Trips | Majority within Europe (~70%) | Estimated 30% outside Europe |
| Most Visited Non-European Country | – | United States |
- An Overview of Italian Inbound Tourism in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka marked a significant milestone in its tourism recovery, recording the highest monthly tourist arrivals for 2024 in December, with 248,592 visitors. For the entire year, 2,053,465 tourists visited Sri Lanka, reflecting a 38% increase compared to 2023.
With such a significant growth in tourist arrivals, India remained the top source market, with arrivals increasing from 116,193 in 2023 to 184,468 in 2024. Other countries, such as the United Kingdom, Germany, and China, also showed substantial increases in tourist numbers during this period.
Table 3: Tourist Arrivals from Different Tourist Generating Source Markets
| Rank | Country | Tourist Arrivals (Jan-Jun 2023) | Country | Tourist Arrivals (Jan-Jun 2024) |
| 1 | India | 116,193 | India | 184,468 |
| 2 | Russian Federation | 110,275 | Russian Federation | 114,104 |
| 3 | United Kingdom | 50,822 | United Kingdom | 89,352 |
| 4 | Germany | 45,197 | Germany | 70,070 |
| 5 | China | 19,862 | China | 63,816 |
| 6 | France | 27,588 | France | 49,340 |
| 7 | Australia | 26,898 | Australia | 40,746 |
| 8 | United States | 21,766 | United States | 32,717 |
| 9 | Poland | 6,341 | Poland | 23,896 |
| 10 | Maldives | 13,909 | Maldives | 23,803 |
| — | Italy | 22242 (66% % Change 2022/23) | Italy | 24,200 (est.) |
Source: Sri Lanka Tourism Development Authority, 2024
Italian tourist arrivals to Sri Lanka have experienced fluctuations over the past years, influenced by various global events and travel trends.
In July 2023, Sri Lanka received 5,737 Italian tourists, followed by 4,455 in August 2023. These numbers indicate a steady interest from Italian travelers and on average annually nearly 22,000-24,000 Italian inbound tourists visit to Sri Lanka contributing for a significant positive impact to Sri Lanka’s tourism industry.
It is obvious that Italian outbound tourism is experiencing robust growth, surpassing pre-pandemic levels with different travel motives including traditional leisure travel dominating preferences, particularly sun and beach holidays.
- The Future of Tourism: Embracing Readiness for Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable tourism is a comprehensive approach that covers all aspects of the tourism experience, addressing economic, social and environmental concerns. Its primary goal is to ensure the long-term sustainability of tourism activities by delivering overall benefits to the development and protection of social, economic, natural and cultural environments of destinations.
The UN-Tourism emphasizes an urgent need for all tourism destinations to universally adopt sustainable tourism principles when promoting tourism with any type by ensuring a well-balanced approach through simultaneously integrating the environmental, economic, and socio-cultural aspects of tourism development.
“Tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities”. (https://www.unwto.org/sustainable-development)
According to Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC), “It is an aspiration to acknowledge all the impacts of tourism, both positive and negative. It aims to minimize the negative impacts and maximize the positive ones” (https://www.gstcouncil.org/what-is-sustainable-tourism/).
Tourism development demands cross-sector collaboration and inter-sectoral partnership with inclusive engagement and strategic planning.
- Sustainable Tourism and Glocalization
The concept of “Glocalization,” which combines global trends with local adaptations, is increasingly relevant in the tourism sector. The concept of “Glocalization” derived the transformation – “From Local to Global” seeming a conceptual reversal kind of Globalization – “From Global to Local”.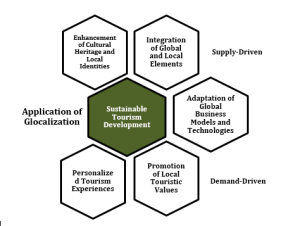
In another word, Glocalization is the promotion of local products or services for global market by capitalizing increasing global market trends and technological innovations, without unchecked and unbridled “Visionless Imitations”.
Glocalization and sustainable tourism are mutually reinforcing, interdependent and interconnected. Appropriate application of glocalization process is a decisive factor to determine the diversity, authenticity and uniqueness of tourism attractions in any destination in global tourism.
- Key Advantages of Glocalization for Sustainable Tourism Development
Glocalization ensures that global sustainability efforts are effectively customized for local sustainability contexts. It fosters tourism that must be both globally responsible and locally beneficial, balancing between the requirements in the Application of 3E Concepts: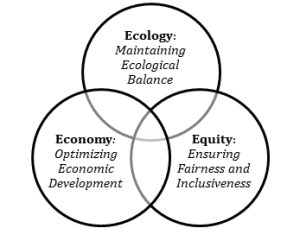
Furthermore, globalized tourism highlights the adapting of global frameworks to local contexts in sustainable tourism practices. Collaborative partnerships among stakeholders such as government authorities, I/NGOS, cooperation and businesses and community are crucial to creating a balanced approach that meets the needs of both global travelers and locals of a destination in a sustainable manner.
Table 4: Key Characteristics of Glocalized Sustainable Tourism
| Globalized Tourism Demand | Glocalized Tourism Supply | |
| Key Characteristics | · Increasing global tourist preferences and responsible behaviors for sustainable tourism products and applications | · Ensuring the international qualities, standards and certification in promoting sustainable tourism practices along with:
– Local Values, – Local Heritage – Local Livelihood Styles – Local Wisdom, – Local Identities Socially and Culturally Uniqueness – Local Needs, Requirements and Expectations |
| Key Drivers | · Higher Disposable & Discretionary Income Levels,
· More Educated Tourists · Greater Awareness of Sustainability Practices · Increasing Trends in Responsible Consumption and Uses in Tourism · More Demand for Personalized, Heterogeneous and Authentic Tourism Experiences · Increased Global Travel Mobility and Technological Advancement |
· Global Recognition of Inclusive, Integrated and Sustainable Tourism Development
· Encouraging Industry-Policy Initiations for Sustainable Tourism Practices at National and International Levels in Many Destinations · Promotion of Local & Regional Tourism Accompanied by Different Alternative Tourism · Empowering Local Communities through their Cultural Heritage . |
- “Push” and “Pull” Factors of Glocalization for Sustainable Tourism Development
Main Push and Pull Factors to visit different destinations by Italian outbound tourists such as visa-free access facilities, socio-demographic transitions of Italian tourists, cultural and natural attractions of destinations, changing discretionary income levels, improving travel transport, communication information facilities including social and digital marketing strongly influence the destination choices in Italian outbound tourism development.
Along with such driving forces, there is an increasing interest in sustainable, nature-based experiences and cultural immersion by Italian travelers. Italian tourists’ spending in abroad on sustainable tourism experiences is substantially high and heavily influenced by destinations’ rich cultural heritage and natural beauty with an increasing demand.
Italian tourism sector is also increasingly focused on sustainability, driven by both environmental concerns and evolving traveler preferences (https://markwideresearch.com/italy-sustainable-tourism-market/). Recent data indicates a growing trend towards conscious tourism, with travelers seeking eco-friendly options and authentic local experiences (https://www.walksofitaly.com/blog/travel-tips/sustainable-tourism-in-italy).
Italian travel motives are increasingly driven by a strong desire for sustainability, with a majority preferring eco-friendly accommodations and showing a willingness to adopt sustainable practices like using public transport and supporting local communities (https://www.statista.com/topics/6463/sustainable-tourism-in-italy/). Environmental consciousness, particularly related to climate change, influences travel decisions, with many seeking to protect the territory and reduce its ecological footprint.
With such a shift incorporating Italian tourists’ preferences for nature, local culture, and authentic experiences, including culinary tourism focused on local and organic cuisine, growing support of Italian tourism sector can be seen for sustainability criteria in travel planning and a notable rise in train travel as a greener alternative.
Table 5: Recent Initiations Implemented to Promote Sustainable Tourism Practices in Italian Tourism:
| Policy/Initiative | Objective | Implementation Details |
| Italy’s Strategic Tourism Plan 2023-2027 | · This focuses on revitalizing the tourism sector through five key pillars: governance, innovation, quality and inclusion, training and professional tourism careers and sustainability.
· It includes initiatives for various tourism segments and establishes a Tourism Digital Hub (TDH) to connect tourists with the Italian tourism ecosystem by digitalizing services, aggregating data, and fostering collaboration among tourism stakeholders. |
· The plan has a total allocation of €114 million14 |
| Sustainable Tourism Fund | · Promote innovative tourist itineraries, deseasonalization, intermodal tourism and sustainability certifications. | · €25 million budget over three years (€5 million for 2023, €10 million each for 2024 and 2025). Grants available for businesses to support these objectives. |
| Strategic Plan for Innovation & Research in Agriculture-Food Sector (2017-2022) | · Promote sustainable consumption and production practices within agriculture linked to tourism.
· Enhance local food systems supporting agritourism activities. |
· Supports local handicrafts recovery, traditional crafts preservation and environmental protection through sustainable agriculture practices. |
| Italy’s Tourism Strategy Plan (2017-2022) & Beyond 2022 | · Initiatives continue focus on sustainability through enhancing skills development in the sector;
· Improve quality of services while promoting environmental sustainability · Preserve cultural heritage sustainably; Encourage technological innovation within the industry. |
· Italy has implemented several strategic tourism plans to enhance the country’s tourism sector.
· The “Efficiency and Sustainability” tourism strategy for 2017-2022 focused on integrating tourism policies with Industry 4.0 and adopting advanced technologies to improve services. · Focused on technological and organizational innovation, skills development, and quality services, all integrated with a sustainable approach to Italy’s environmental and cultural heritage. |
| Art Bonus Decree (2014) | · Support restoration of cultural heritage sites through tax credits.
· Encourage digital tourism activities. |
· Tax credits are provided for restoring public cultural patrimony and supporting digital tourism initiatives. |
| National Plan for Tourism Mobility (2014) | · Improve transportation infrastructure to enhance mobility in southern regions. Foster bike tourism and other slow travel options. | · Part of the Art Bonus Decree aims at developing sustainable transport options. |
Source: AI Search from https://www.perplexity.ai/search/edit-below-as-far-as-the-infor-j378iTa_R1e2N_8nt.Ngng
- Bridging Expectations of Italian Tourists
Recent data from various sources highlights the demand patterns of Italian tourists that have significantly stimulated sustainable tourism practices in both domestic and outbound travels of Italian tourists in global tourism.
Key demand patterns of Italian tourists on sustainable practices can be summarized as below:
| Growing Interest in Sustainability: | About 60% of Italians consider environmental factors when planning trips. |
| Eco-Friendly Accommodation Choices: | Increased preference for agritourism and certified green hotels.
80% of Italians prefer certified environmentally friendly accommodations even at the same cost. |
| Climate Change Awareness: | 64% are influenced by climate change to travel sustainably. This rises to 71% among those under 25. |
| Sustainable Travel Options: | Favor train travel as an eco-friendly alternative to cars for domestic trips. |
| Cultural Experiences: | Seek authentic experiences that support local communities, aligning with sustainable tourism. |
| Nature-Based Activities: | Popular activities include hiking and cycling among environmentally conscious travelers. |
| Motivations for Sustainable Tourism: | Key drivers include protecting the territory (60%) and reducing environmental impact through eco-friendly transport (52%). |
| Influence of Sustainability on Travel Decisions: | 72% of travel decisions consider sustainability criteria (transport, destinations, accommodations, etc.). |
| Interest in Nature and Local Culture: | Tourists show increased interest in nature and exploring villages and small towns. |
| Sustainable Dining Preferences: | Restaurants prioritizing locally sourced and organic ingredients attract sustainable food enthusiasts |
| Preferred Tour Operators: | Tour operators promoting cultural understanding and supporting local communities are favored by conscious travelers. |
- Matching the Trends and Fashions for Powering Italian Inbound Tourism in Sri Lanka
Discussions with key informants regarding Italian inbound tourism in Sri Lanka reveal several attractive places and activities tailored to the travel interests of Italian inbound tourists in Sri Lanka.
- Sri Lanka offers a diverse range of attractions and activities that are highly appealing to Italian inbound tourists. Eco-friendly accommodations, particularly luxurious and semi-luxurious eco-lodges like the Rainforest Ecolodge in Sinharaja and Flameback Ecolodge in Weerawila, cater to sustainability-focused travelers.
- The sunny and pristine beaches of Mirissa, Hikkaduwa, Hiriketiya, Dickwella, Unawatuna, and Arugam Bay are trendy spots for relaxation and water-based activities.
- Nature-based experiences such as hiking and cycling on scenic trails in Ella, wildlife safaris in Yala National Park, and responsible whale watching in Mirissa and Trincomalee further enhance the appeal.
- Cultural interactions at iconic sites like Galle Fort, Sigiriya, and Polonnaruwa, along with tea plantation tours in Kandy and village visits showcasing traditional crafts, provide immersive experiences.
- Marine conservation activities like snorkeling at Pigeon Island and visiting turtle hatcheries in Kosgoda align with sustainable tourism interests.
- Additionally, promoting restaurants that prioritize locally sourced ingredients and encouraging eco-friendly transportation options like train travel help minimize environmental impact while connecting major destinations.
However, promotion of sustainable tourism practices is more decisive to attract for high-end and responsible Italian tourists under their ongoing demand trends and travel behaviour at present. For this purpose, the following can be recommended:
(i). Commitment to Sustainability:
- Sri Lanka must dedicate to sustainable tourism practices, showcasing eco-friendly accommodations such as certified green hotels and agritourism options. Initiatives that protect local ecosystems and cultural heritage resonate with the growing interest in sustainability among Italian tourists.
- (ii). Eco-Friendly Accommodations:
A diverse range of certified environmentally friendly lodging options is essential, emphasizing energy efficiency and local sourcing. Unique stays, like eco-lodges or farm stays, allow tourists to immerse themselves in local culture while minimizing their environmental impact. - Nature-Based Activities:
Developing packages for hiking, cycling, and wildlife tours caters to environmentally conscious travelers. Opportunities to explore Sri Lanka’s diverse landscapes, including national parks and coastal areas, align with tourists’ love for nature. - Cultural Experiences:
Authentic cultural experiences that support local communities, such as cooking classes with local chefs and traditional craft workshops, enhance the appeal of Sri Lanka. Encouraging interactions with local communities fosters cultural understanding and appreciation. - (v). Sustainable Transportation Options:
Promoting sustainable travel options within Sri Lanka, such as train travel or guided eco-tours, reduces reliance on cars. Providing information on public transportation systems and eco-friendly transport alternatives facilitates easier travel around the country. - Local Cuisine:
Highlighting restaurants that prioritize locally sourced and organic ingredients appeals to Italian tourists’ interest in sustainable dining. Promoting food festivals or culinary tours that focus on traditional Sri Lankan cuisine and local farming practices can further enhance their experience. - Collaboration with Tour Operators:
Partnering with tour operators who emphasize sustainability and cultural understanding ensures that experiences resonate with the values of Italian travelers. - Digital Marketing Strategies:
Utilizing social media and digital platforms to share stories about sustainable tourism initiatives in Sri Lanka can engage potential visitors. Creating compelling content that highlights the beauty of Sri Lanka’s nature, culture, and commitment to sustainability will attract more tourists. - Education and Training:
Promotion of the Italian language and cross-cultural understanding can enhance communication, foster cultural exchange, create tailored experiences, and build partnerships in Sri Lanka’s tourism sector, ultimately promoting Indian inbound tourism by making the destination more accessible and appealing to Italian travelers.
By focusing on these strategies, Sri Lanka can effectively promote itself as a premier destination for sustainable tourism, appealing to the values of Italian travelers.







