Micro Plastics – Are we Breathing , Drinking and Eating plastics?


Plastics have become part and parcel of our day to day lives. At present plastics are heavily misused, or over used unnecessarily. This situation has created many environmental and health issues. 350 million tons of plastics are produces annually in the world and it is expected that this amount will be threefold by the year 2050. At present 9% plastics are recycled and 12% of them are incinerated or burnt under controlled conditions, whereas 8% is dumped in the sea.
Facts about Plastics:
- 10% of the waste generated are plastics
- 500 billion plastic bags are used per year world wide
- 13 million tons of plastic waste is added to the sea annually.
- 01 million plastic bottles are bought every minute around the world.
- By products of 17 million crude oil barrels are required for annual production of plastics.
- Around 100,000 sea animals are killed annually due to plastic waste.
- It takes more than 100 years to decay plastics.
- 50% of the plastic production is single use plastics. ( Used only once and disposed) Source-United Nations Environment Programme ( UNEP)
What are food grade plastics?
All types of plastics are not suitable to be used as food containers or used in food wrapping. The recommended types are PET, HDPE,LDPE and PP. PVC and Polystyrene plastics are not suitable for food wrapping or as food containers, as they are toxic. The following symbol has to be used in food grade plastics. Some plastics contain toxic chemicals like Bisphenol A, which are known as endocrine disruptors.

What are Micro Plastics?
Plastics which are less than 5 mm in diameter are known as micro plastics. These can be of two types, primary micro plastics and secondary micro plastics. Plastics that are commercially produced with diameter less than 5mm are primary micro plastics. Micro plastics generated by breaking of plastics or from degraded plastics are known as secondary micro plastics. They can be produced in washing synthetic clothes, breaking of plastic utensils, toys or degradation of other plastic objects.
Recent research has shown that both primary and secondary micro plastics are commonly found in marine environment. Micro beads, a category of primary micro plastics found in various products. Eg. cosmetic products like facial scrubs, tooth paste etc. These get in to the marine environment through waste water streams.

Micro plastics have been found in fish and also in human faeces, which ensures that micro plastics are getting in to our bodies through inhalation, or ingestion through food or water.
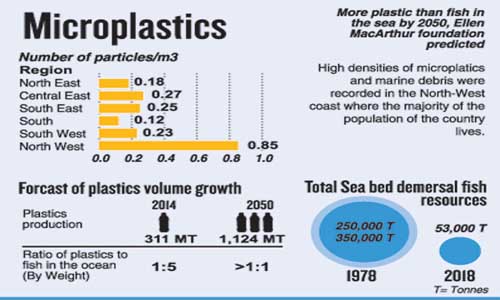
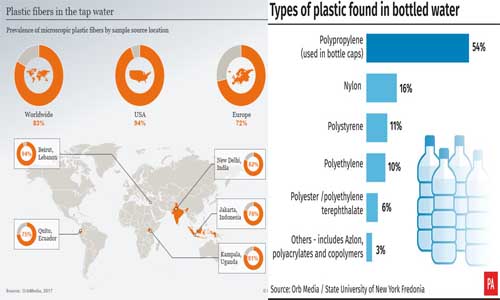
According to research drinking water is contaminated with micro plastics world over, where both tap water and bottled water are contaminated with micro plastics.
Research on impacts caused due to ingestion of plastics has been carried out in animals. At present human studies are on going and World Health Organization (WHO) has raised its concern on this issue.
Plastic Recycling for managing plastic waste
Waste plastics can be heated and made in to plastic pellets or small pieces. These can be used in making new plastic products, which is known as recycling. There are around 150 plastic collectors and recyclers registered under the Central Environmental Authority, but there are many more who have not registered. Some of the major issues in the recycling industry at pesent are the poor collection system of waste plastics, the price fluctuations in the recycled plastics, labour and the other costs that has to be incurred in transportation of waste plastics, categorization of plastics for recycling, cleaning of dirty plastics and accumulation of non recyclable plastic items due to the lack of technology. Government is facilitating the recyclers by provision of equipment, awareness creation and training.

What are Bio-degradable Plastics?
These plastics are made of vegetative material which decomposes. Therefore these products are environment friendly.

Some of the main steps that can be taken to improve plastic waste management .
- Avoid misuse/ overuse of plastics
- Avoid haphazard disposal of plastics and littering.
- Use alternatives for plastics as much as possible
- Use only recyclable plastics and ensure they are recycled.
- Avoid usage of disposable (single use) plastics. ( Straws, cups etc)
- Promote bio-degradable plastics.
- Redesign products to minimize plastic packaging material
- Practice waste segregation to segregate plastics.
- Adhere to plastic management regulations.
Mrs. Sujeewa Fernando
Assistant Director
Environment Pollution Control and Chemical Management Division Ministry of Environment






